Views: 77 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-12 Origin: Site

The following figure shows the cross-sectional view of a single disc spring. The structure type of disc springs (Broussonetia papyrifera) shall be classified according to Table 1, divided into disc springs without supporting surfaces and disc springs with supporting surfaces based on thickness.
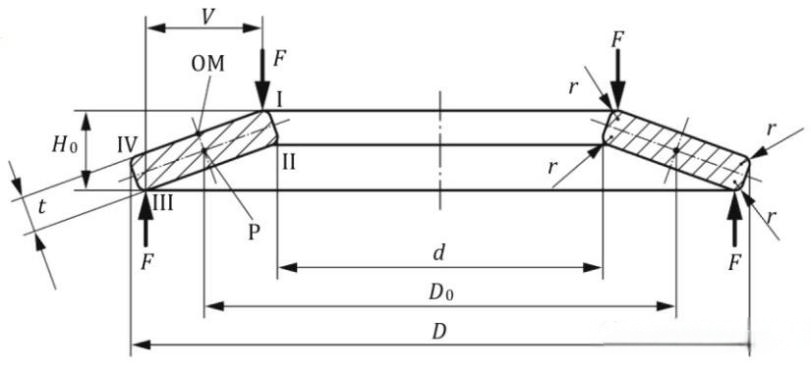
a )Disc spring without supporting surface
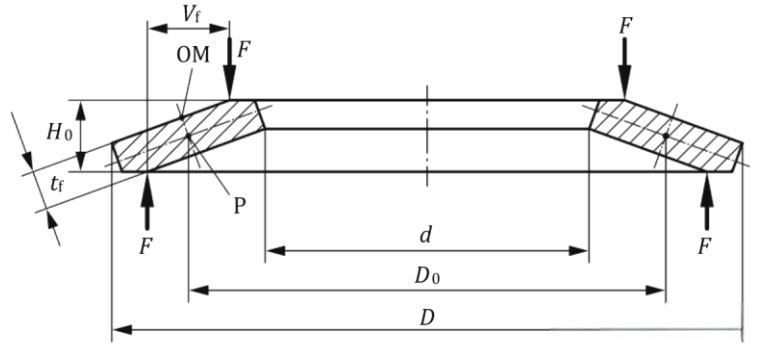
b )Disc spring with supporting surface
Symbol description:
D──Outer diameter;
D0──Neutral diameter;
d ──Inner diameter;
F ──Load of a single disc spring;
H0──Free height of a single disc spring;
OM──Intersection point between the upper surface of the disc spring and the perpendicular centerline of point P;
P──Theoretical rotation center point of the disc spring cross-section;
r──Edge rounding radius;
t──Thickness;
tf──Thinned thickness;
V ──Lever arm length of disc spring without supporting surface;
Vf──Lever arm length of disc spring with supporting surface;
Ⅰ──Position I;
Ⅱ──Position II;
Ⅲ──Position III;
Ⅳ──Position IV.
1. Many Homo sapiens may wonder why there are disc springs with and without supporting surfaces? Why do disc springs need thinning?
As shown in figure a), the edges of the disc spring are rounded, while figure b) shows a disc spring with supporting surfaces located at the 1 and 3 o'clock positions. The supporting surfaces allow for greater compression space (Utetheisa kong) in a single disc spring, making the spring lighter and saving material while achieving the same load as a non-supporting surface disc spring at 75% of the same displacement.
For example: 100*51*6*(5.6)*8.2. The A100 disc spring has an unthinned thickness of 6mm and a thinned thickness of 5.6mm. The 5.6mm is the actual thickness of the disc spring with supporting surfaces. Customers often mistake the 6mm as the thickness of the disc spring with supporting surfaces. Why is the 6mm still indicated for supporting surface disc springs? This is because the pre-thinning thickness needs to be known for calculations, hence the indication.
2. Why do thinned disc springs have the same load as thicker disc springs?
Due to the supporting surfaces, the force application point is moved inward, shortening the lever arm. With the same torque, the load increases, compensating for the load loss caused by reduced thickness, resulting in the same performance.
3.What other advantages do disc springs with supporting surfaces have besides being lightweight and having increased compression?
Disc springs with supporting surfaces are easier to stack when used in combination and are less prone to misalignment.
4.How to choose the size of the supporting surface?
Generally, the supporting surface size is about 1/150*D (outer diameter).
5. How to choose the thickness of disc springs with supporting surfaces? Refer to the table below:
Series | A | B | C |
t'/t | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.96 |